Table of Contents
When Monitoring Receding Gums Is Enough
When to Prioritize Treatment for Receding Gums
When Receding Gums Require Urgent Treatment
Why Some Cases of Receding Gums Worsen Faster
What to Do if You’re Concerned About Receding Gums
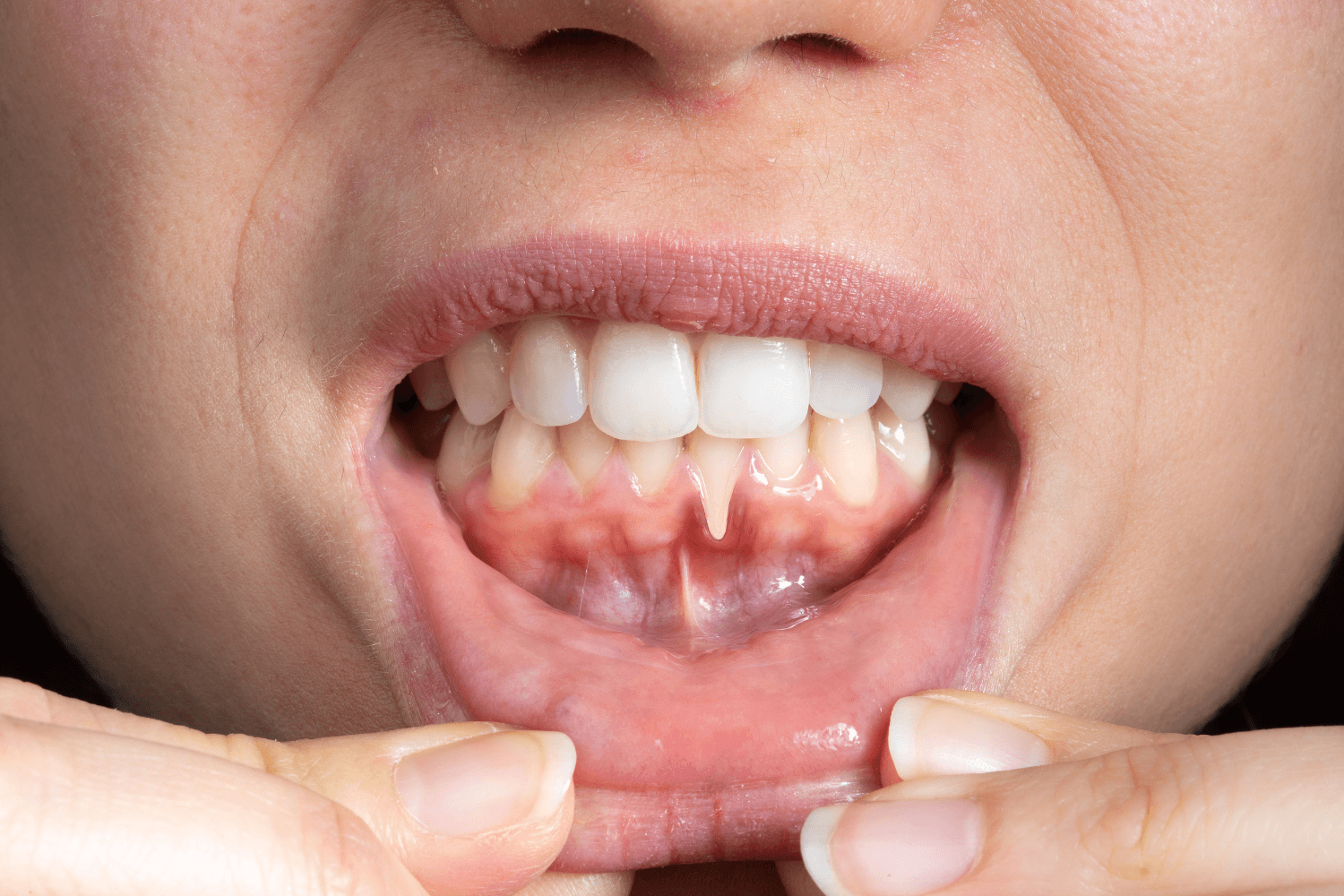
You might notice your teeth looking slightly longer than they used to, or a sharp twinge when cold water hits a specific spot. Receding gums often show up this way, quietly and without much warning.
Gum recession is a common dental concern, and while it can look alarming, it doesn’t always require immediate treatment. In many cases, gum recession progresses slowly and can be safely monitored with guidance from your dentist. In other situations, early treatment is important to prevent sensitivity, decay, or long term damage to the teeth and supporting bone.
When Monitoring Receding Gums Is Enough
A small amount of gum recession does not automatically call for treatment. In many cases, careful monitoring during regular dental visits is the right place to start. This approach is typically recommended when the recession appears stable and is not affecting comfort or oral health.
Monitoring is often appropriate when these signs are present:
- Minimal recession (1 to 2 mm): A small amount of recession is common and is often only noticeable during a dental exam. If the surrounding gum tissue is healthy and pink, this level of change is usually not a concern.
- No progression over time: When measurements remain the same across multiple visits, it suggests the recession has stabilized rather than continued to advance.
- No sensitivity or pain: When exposed areas are comfortable during eating, drinking, and brushing, treatment can often wait.
- Good oral hygiene: Firm, pink gums that do not bleed are a sign that active disease is not contributing to the recession, which makes monitoring a safer option.
Even if your situation is considered low-risk, you’ll want to keep up with regular checkups. These visits allow us to track small changes and confirm that the condition remains stable.
Temporary factors can also influence gum health. Changes in diet, new medications, or shifts in overall health sometimes affect the gums, which makes open communication with your dental provider important.
Even if your situation is considered low-risk, you’ll want to keep up with regular checkups. These visits allow us to track small changes and confirm that the condition remains stable.
Temporary factors can also influence gum health. Changes in diet, new medications, or shifts in overall health sometimes affect the gums, which makes open communication with your dental provider important.
What Do We Mean By “Monitoring”?
Monitoring does not mean ignoring the problem. It means tracking it closely. During routine visits, we’ll take precise measurements to track any changes and we’ll discuss your home care routine.
This approach is about teamwork, which means we watch the clinical signs while you pay attention to any new sensitivity or visible changes at home.
When to Prioritize Treatment for Receding Gums
Sometimes, monitoring isn’t enough. As gum recession progresses, it can shift from being a minor observation to a problem that affects comfort and long-term tooth health.
When that happens, treatment becomes part of the conversation. You don’t necessarily need to call us for an emergency appointment, but you should schedule a visit to review options and prevent further damage.
Treatment is more likely to be recommended when these signs appear:
- Moderate and progressing recession (3 to 4 mm): This level of recession is more significant, especially when measurements increase between visits. Continued movement signals an active issue that benefits from intervention.
- Increased tooth sensitivity: As the root surface becomes exposed, sensitivity often follows because it lacks protective enamel. Discomfort during eating, drinking, or brushing is a common reason to move forward with treatment.
- Aesthetic concerns: Recession on visible teeth can make the smile look uneven or darker at the gum line. Addressing appearance is not superficial; it often improves comfort and confidence at the same time.
- Difficulty keeping the area clean: Exposed root surfaces can develop grooves that trap plaque. When home care becomes harder despite good habits, the risk of decay rises, making treatment a preventative step.
At this stage, treatment may involve several approaches. We might recommend desensitizing agents, tooth-coloured bonding to protect the exposed root, or gum grafting to replace lost tissue and improve stability.
In some cases, more than one approach is used. Recommendations depend on the cause of the recession, how active it is, and how the tooth is responding over time.
Changes to daily oral care are often part of the plan as well. Adjusting brushing technique or using targeted products like fluoride varnish or prescription toothpaste can help protect exposed root surfaces and reduce irritation.
When Receding Gums Require Urgent Treatment
In some cases, receding gums point to a more serious underlying problem. This is the point where monitoring or routine treatment is no longer enough, and action is needed to protect the teeth and supporting structures. Urgent situations are usually tied to active disease or a high risk of permanent damage.
Urgent treatment is more likely when the following signs are present:
- Severe recession with root exposure (5 mm or more): At this level, a large portion of the tooth’s root is exposed. The tooth becomes more vulnerable to sensitivity, decay, and structural damage.
- Active gum disease (periodontitis): Red, swollen gums that bleed easily, along with deep pockets around the teeth, indicate an active infection. Gum disease is a major driver of recession and must be treated promptly to prevent continued tissue and bone loss. Periodontitis is common, particularly as we age. Nearly half of adults over 30 have some form of gum disease.
- Tooth mobility: Movement in a tooth, even slight movement, signals a loss of support from the surrounding gum and bone. Without treatment, the risk of tooth loss increases.
- Rapid progression: Visible changes in the gum line over a short period of time suggest an aggressive process that requires quick intervention.
Urgent care focuses first on treating the cause. When gum disease is involved, this often begins with deep cleaning procedures such as scaling and root planing to control infection. Once inflammation is managed, additional treatment may be recommended to protect exposed roots and improve stability.
In more advanced cases of gum disease, care may involve coordination between a general dentist and a periodontist. When infection is present, antimicrobial rinses or antibiotics may also be used to reduce bacterial load and support healing.
Why Some Cases of Receding Gums Worsen Faster
Several factors influence how quickly receding gums progress and how urgently treatment may be needed. Some are tied to daily habits, while others relate to biology or overall health.
Aggressive Brushing
Brushing with too much force or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can gradually wear away gum tissue. This type of mechanical irritation is a common cause of recession. Switching to a soft bristled brush and using a lighter technique often helps slow or stop further changes.
Grinding or Clenching (Bruxism)
Grinding places significant pressure on the teeth and the structures that support them, including gum tissue and bone. Over time, this stress can accelerate recession. A custom nightguard is often recommended to reduce force and protect both teeth and gums.
Smoking and Tobacco Use
Tobacco restricts blood flow to the gums, which limits healing and weakens the body’s response to infection. As a result, recession tends to progress more quickly and treatments are often less effective. Quitting tobacco use has a direct impact on gum health and treatment outcomes.
Genetics
Some people naturally have thinner or more fragile gum tissue, which makes recession more likely regardless of oral hygiene habits. A family history of gum disease or recession can increase risk, though it does not guarantee the same outcome.
Other Health Related Factors
Hormonal changes, certain medical conditions such as diabetes, and environmental exposures can all affect gum health. These influences may increase vulnerability to recession or change how the tissue responds to treatment.
Sharing a complete health history with your dental provider allows these factors to be considered when recommendations are made and helps ensure that care decisions are based on the full picture.
What to Do if You’re Concerned About Receding Gums
Receding gums don’t all follow the same path. Some cases stay stable for years, while others need attention to prevent sensitivity, decay, or tooth loss. The difference usually comes down to careful evaluation and timing.
If you’ve noticed changes in your gums, an exam can clarify what’s happening and whether monitoring or treatment makes sense. Measurements, X-rays, and a review of contributing factors provide a clear picture.
To schedule an evaluation, contact Somerset Dental on James. We’ll assess your gum health and talk through appropriate next steps based on what we see.